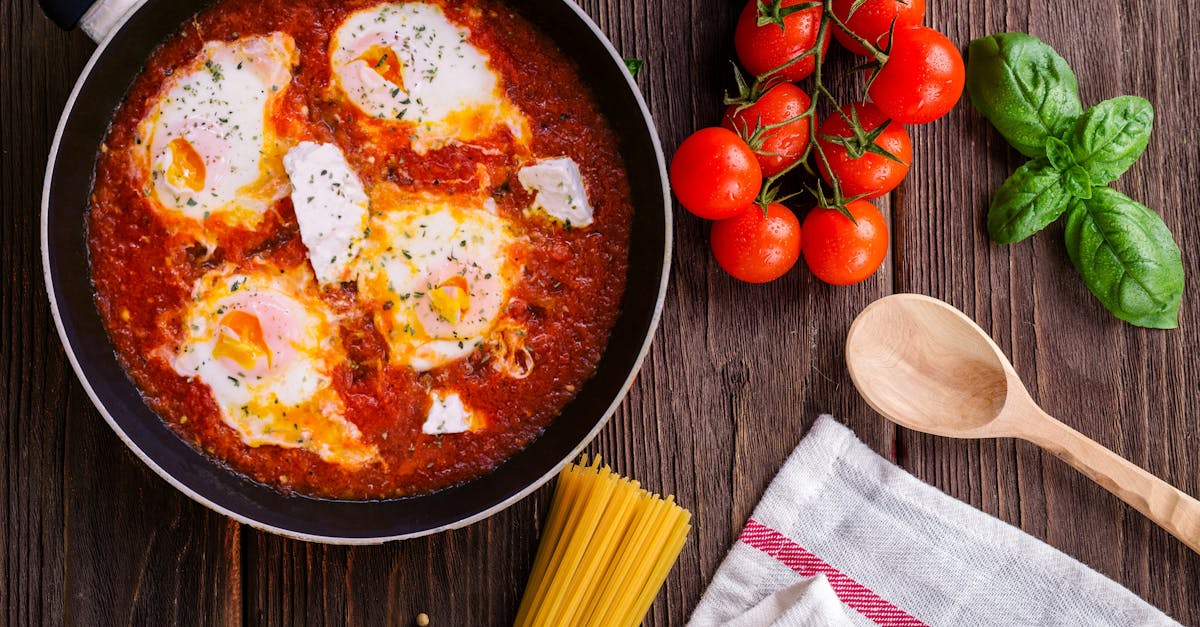
Fermented eggs are a unique and flavorful way to enjoy this everyday ingredient. This ancient preservation method enhances the eggs with a tangy, savory depth that’s perfect for adventurous eaters and culinary explorers alike. Fermentation not only boosts the flavor but also adds beneficial probiotics that support gut health.
Ingredients
To prepare our fermented eggs, we will need a precise combination of fresh eggs and fermentation components that ensure flavor development and optimal probiotic growth. Here is everything required to start the fermentation process effectively:
- Fresh eggs (preferably free-range or organic) — 6 large
- Salt (non-iodized, such as sea salt or kosher salt) — 1/2 cup
- Water (filtered or distilled) — 4 cups
- Rice bran or ash (optional, traditional fermenting medium) — 2 tablespoons
- Vinegar (rice vinegar or white vinegar) — 1 tablespoon
- Garlic cloves (peeled and crushed) — 2
- Bay leaves — 2 leaves
- Peppercorns (whole) — 1 teaspoon
| Ingredient | Quantity | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh eggs | 6 large | Use fresh, high-quality eggs |
| Salt | 1/2 cup | Non-iodized sea or kosher salt |
| Water | 4 cups | Filtered or distilled |
| Rice bran or ash | 2 tablespoons (optional) | Traditional medium, enhances fermentation |
| Vinegar | 1 tablespoon | Adds acidity to balance fermentation |
| Garlic cloves | 2 cloves | Peeled and crushed for flavor |
| Bay leaves | 2 leaves | Adds aromatic notes |
| Peppercorns | 1 teaspoon | Whole for subtle spice |
By assembling these ingredients carefully, we set the foundation for a successful fermentation process resulting in savory, tangy eggs rich in probiotics.
Equipment Needed
To successfully prepare fermented eggs with rich flavor and optimal probiotic benefits, we must equip ourselves with the right tools. Using precise equipment ensures controlled fermentation and food safety throughout the process. Below is a detailed list of essential items along with their purposes:
| Equipment | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Glass jar with airtight lid | Creates an anaerobic environment for fermentation to prevent contamination and preserve flavor |
| Non-reactive bowl | For mixing non-iodized salt and water; plastic or glass preferred to avoid metallic taste |
| Measuring spoons and cups | Ensures accurate measurement of ingredients critical for successful fermentation |
| Clean cloth or cheesecloth | Covers the jar during initial fermentation to allow airflow while keeping debris out |
| Weight or fermentation stone | Keeps eggs submerged in brine, preventing exposure to air and mold formation |
| Sterilized tongs or fork | Used to gently place and remove eggs without contaminating the brine |
| Thermometer (optional) | Monitors ambient temperature; ideal fermentation happens between 65°F and 75°F (18°C – 24°C) |
| Labeling materials | Records start date and batch details to track fermentation duration |
“Using the correct equipment minimizes risks and maximizes the development of the tangy, savory flavor our fermented eggs are known for.”
For us, keeping the eggs fully submerged and maintaining a clean fermentation environment is vital. A suitable jar with a secure lid paired with a proper weight allows the natural fermentation process to flourish, encouraging the growth of beneficial probiotics.
Having these tools ready and sterilized is fundamental before beginning the fermentation, ensuring that our fermented eggs develop a safe texture and complex flavor profile.
Prep Work
To achieve the best results with our fermented eggs recipe, thorough preparation is crucial. We carefully prepare each component to ensure optimal fermentation, flavor, and safety.
Preparing the Eggs
- Select fresh, free-range or organic eggs to guarantee quality and reduce contamination risks.
- Rinse the eggs gently under filtered water to remove any dirt or debris without removing the natural protective coating.
- Pat the eggs dry with a clean towel.
- Inspect each egg for cracks or imperfections. Discard any damaged eggs as they may compromise the fermentation process.
- To minimize bacteria on the shell, we lightly sanitize the eggs by wiping them with a cloth dipped in a vinegar-water solution (1 part vinegar to 3 parts water).
- Allow the eggs to dry completely before placing them in the fermentation vessel.
Preparing the Brine
A well-balanced brine ensures the perfect environment for the fermentation process and probiotic development.
| Ingredient | Quantity | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Filtered water | 4 cups (1 liter) | Base of the brine |
| Non-iodized salt | 3 tablespoons | Prevents harmful bacteria |
| Rice bran or ash* | 2 tablespoons | Enhances fermentation and flavor |
| Garlic cloves | 2-3, crushed | Adds aroma and flavor |
| Bay leaves | 1-2 | Adds depth to taste |
| Peppercorns | 5-6 | Adds mild spiciness |
*Optional but recommended for authentic flavor and culture.
Steps:
- Warm the filtered water slightly (not boiling—around 100°F or 38°C) to dissolve the salt fully.
- Stir in the non-iodized salt until completely dissolved.
- Add the rice bran or ash and mix thoroughly.
- Incorporate the crushed garlic cloves, bay leaves, and peppercorns into the brine.
- Let the brine cool completely to room temperature before use to avoid cooking the eggs.
By meticulously preparing the eggs and crafting the brine with precision, we set the foundation for a flavorful and probiotic-rich batch of fermented eggs.
Instructions
Follow these detailed steps to create perfectly fermented eggs bursting with tangy flavor and rich in probiotics. Precision and care in each stage ensure a safe, savory result.
Fermentation Process
- Prepare the Eggs
- Select fresh, high-quality eggs free of cracks.
- Gently rinse under cool water to remove surface dirt.
- Lightly sanitize by dipping in a vinegar-water solution (1 part vinegar to 3 parts water).
- Let eggs air dry completely on a clean towel.
- Mix the Brine
Combine the brine ingredients in a non-reactive bowl:
- Filtered water
- Non-iodized salt
- Rice bran or wood ash (as a fermentation enhancer)
- Garlic cloves
- Bay leaves
- Whole peppercorns
- Pour Brine and Submerge Eggs
- Place eggs carefully into your sterilized glass jar.
- Pour brine over eggs ensuring they are fully submerged.
- Use a weight or fermentation stone to keep eggs below brine surface—critical for preventing mold.
- Seal and Store
- Seal jar with an airtight lid to maintain an anaerobic environment.
- Store at a consistent temperature between 65°F and 75°F (18°C to 24°C) away from direct sunlight.
- Monitor Fermentation
- Fermentation typically takes 14 to 21 days.
- Check daily for brine level and remove any surface scum with sterilized tongs if necessary.
- Do not disturb eggs unnecessarily to avoid contamination.
| Step | Action | Key Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Prepare eggs | Rinse, sanitize, dry | Use vinegar-water dip |
| Mix brine | Combine salt, water, rice bran, spices | Use filtered water |
| Submerge eggs | Place eggs in jar, cover with brine | Use weight for full submersion |
| Seal & store | Airtight lid, store at 65°F-75°F | Avoid sunlight |
| Monitor | Check daily, remove scum if present | Do not disturb eggs |
Storing the Fermented Eggs
- After fermentation is complete, move the jar to the refrigerator to slow down the fermentation process and preserve freshness.
- Optimal serving period is within 1 to 2 months for best flavor and probiotic activity.
- Always use sterilized tongs or a clean fork to remove eggs to prevent contamination.
- Store eggs in their brine to maintain moisture and texture.
“Prolonged refrigeration stabilizes flavor and texture while sustaining beneficial probiotics.“
By adhering to these detailed instructions we ensure our fermented eggs develop a unique savory tang combined with a safe, beneficial probiotic profile.
Serving Suggestions
Fermented eggs offer a distinct umami flavor and tangy aroma that elevate many dishes. Here are several creative and delicious ways to enjoy our fermented eggs:
As a Flavorful Snack
Slice the fermented eggs and serve them chilled with a sprinkle of sea salt or a drizzle of soy sauce. Their slightly creamy texture combined with the tangy taste makes for an addictive savory snack.
In Salads and Bowls
Add chopped pieces to salads or grain bowls to introduce a complex probiotic-rich burst. They pair exceptionally well with:
- Mixed greens
- Avocado
- Pickled vegetables
- Quinoa or brown rice
Enhancing Breakfast Dishes
Incorporate fermented eggs by slicing and placing them atop toast, alongside sautéed greens or avocado for a nutritious breakfast packed with flavor and gut-friendly probiotics. Try adding ground black pepper or chili flakes for an extra kick.
In Noodles and Soups
Drop quartered or sliced fermented eggs into ramen, pho, or miso soup right before serving to deepen the broth’s flavor and add texture contrast.
Condiment or Garnish
Mash fermented eggs and mix with a bit of miso paste or mayonnaise to create a tangy spread or dip—ideal for sandwiches or vegetable crudités. Alternatively, sprinkle minced fermented egg over roasted veggies or grilled proteins for a finishing touch.
Serving Tips Table
| Serving Method | Preparation | Pairing Suggestions |
|---|---|---|
| Sliced Snack | Chill and slice | Sea salt, soy sauce |
| Salad/Bowl Addition | Chop into small pieces | Greens, avocado, pickled veggies, grains |
| Breakfast Enhancement | Slice on toast or sides | Sautéed greens, avocado, spices |
| Noodle/Soup Addition | Quarter or slice | Ramen, pho, miso soup |
| Condiment/Garnish | Mash + mix with miso/mayo | Sandwiches, crudités, roasted veggies |
“Fermented eggs bring a unique probiotic punch combined with tangy umami that transforms everyday meals into culinary delights.“
To maintain the best texture and flavor, serve fermented eggs cold or at room temperature, never heated directly, as excessive heat can reduce probiotic benefits and alter the delicate balance of flavors.
Tips for Best Results
To ensure our fermented eggs develop the perfect balance of tangy flavor and probiotic richness, let’s follow these essential tips carefully.
Use Fresh, High-Quality Eggs
Choose fresh, free-range, or organic eggs for the best fermentation outcome. Freshness directly impacts flavor and safety. Before fermentation, always:
- Rinse eggs gently with cold water
- Inspect for cracks and discard any damaged eggs
- Lightly sanitize with a vinegar-water spray (1 part vinegar to 3 parts water) to reduce unwanted bacteria
Maintain Proper Brine Concentration
The brine must have the right salt and ingredient balance to promote beneficial bacteria and inhibit bad microbes. Use:
| Ingredient | Quantity | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Filtered water | 4 cups | Base for brine |
| Non-iodized salt | 3 tablespoons | Controls fermentation, flavor |
| Rice bran or ash | 2 tablespoons (optional) | Enhances fermentation, texture |
| Garlic cloves | 2-3 (crushed) | Adds flavor and antimicrobial properties |
| Bay leaves | 1-2 | Aromatic complexity |
| Peppercorns | 5-6 | Adds mild heat and depth |
Tip: Stir until salt dissolves completely. A consistent brine guarantees even fermentation.
Keep Eggs Fully Submerged
Make sure all eggs remain fully submerged under the brine throughout fermentation. Use a clean fermentation weight or stone to:
- Prevent air exposure that causes spoilage
- Promote anaerobic environment essential for probiotic growth
Check the brine level daily to top off with salted water if needed.
Control Fermentation Temperature
Store the jar at a consistent temperature of 65-75°F (18-24°C). Too warm accelerates fermentation causing off flavors, too cool slows the process down. Avoid sunlight or temperature fluctuations by placing the jar in a pantry or cellar.
Monitor and Maintain Cleanliness
Inspect the jar daily for:
- Surface scum or mold — skim gently with a sterilized utensil if present
- Ensuring no foul odors develop; a pleasant sour smell is expected and desired
Always use sterilized tongs or forks when handling eggs to reduce contamination risks.
Fermentation Timeline
Allow the eggs to ferment for 14 to 21 days for optimal flavor and probiotic content. Taste-test after two weeks to decide if you prefer a milder tang or stronger savory note.
Post-Fermentation Care
Once fermentation reaches your desired taste:
- Refrigerate the jar immediately to slow down fermentation
- Keep refrigerated eggs for up to 1 to 2 months for best quality
Refrigeration preserves texture and probiotic potency.
“Consistency and cleanliness are the cornerstones of successful fermented eggs. Observing these tips ensures a savory, tangy result packed with gut-friendly probiotics.”
By applying these steps carefully, our fermented eggs will develop the signature umami-rich flavor and irresistible aroma every time.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Fermenting eggs can be rewarding but may come with challenges. Below are steps to solve common problems during the fermented eggs recipe process.
1. Eggs Floating or Not Submerged
Keeping eggs fully submerged is critical to prevent spoilage and unwanted mold growth.
- Use a fermentation weight or a clean, sterilized object to keep eggs pressed down in the brine.
- Check brine level daily. If it drops, add salted filtered water (3.5% salinity) to maintain full coverage.
- Avoid using metal weights as they may react with the brine.
“Ensuring eggs stay underwater throughout fermentation creates an anaerobic environment essential for probiotic growth and safe preservation.”
2. Mold Growth on Surface
Surface mold indicates oxygen exposure or impurities.
- Remove visible mold promptly using a sterilized spoon or skimmer.
- Wipe jar rim and lid clean before resealing to maintain an airtight seal.
- Use a clean cheesecloth or lid seal, and ensure utensils are sanitized.
- If mold persists, discard batch and review sanitation steps.
3. Brine Cloudiness or Off Smell
Some cloudiness in brine is normal due to fermentation, but a foul odor signals contamination.
| Symptom | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Excessive cloudiness | Yeast or bacterial overgrowth | Use filtered water; reduce fermentation temperature to 65°F (18°C) |
| Rotten or sulfur smell | Egg spoilage or contamination | Discard batch; sanitize equipment thoroughly next time |
“A pleasant tangy aroma indicates successful fermentation, while unpleasant odors warn of spoilage.”
4. Eggs Cracking During Prep or Fermentation
Cracked eggs compromise brine penetration and safety.
- Inspect eggs carefully for cracks before use.
- Handle gently during rinsing and submersion.
- Use fresh eggs with sturdy shells to minimize cracking risk.
5. Texture Too Rubbery or Chalky
Texture can vary based on fermentation time and ingredient ratios.
- For softer texture, shorten fermentation period to 14 days.
- For firmer texture, extend up to 21 days.
- Adjust salt concentration (3-4%) carefully; too much salt can toughen eggs.
6. Inconsistent Flavor Development
Flavor depends on balance of ingredients and environment.
- Use consistent temperature between 65–75°F (18–24°C).
- Maintain exact brine measurements: 35g salt per 1 liter filtered water.
- Include optional aromatics like garlic or bay leaves as preferred.
- Avoid opening jar frequently, which disturbs fermentation.
By following these troubleshooting tips we ensure our fermented eggs develop the ideal savory tang, safe texture, and probiotic benefits every time.
Conclusion
Fermented eggs open up a world of bold flavors and gut-friendly benefits that can elevate any meal. With careful preparation and attention to detail, we can create a probiotic-rich ingredient that’s both unique and versatile. Whether enjoyed on its own or incorporated into dishes, fermented eggs bring a delicious twist to our culinary adventures. Embracing this traditional preservation method not only diversifies our palate but also supports a healthy digestive system. Let’s keep experimenting and savoring the tangy, savory goodness that fermented eggs have to offer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are fermented eggs?
Fermented eggs are eggs preserved through an ancient fermentation process, enhancing their flavor with tangy and savory notes. This method also introduces beneficial probiotics that support gut health, making them both tasty and nutritious.
What ingredients are needed to make fermented eggs?
You need fresh, preferably free-range or organic eggs, non-iodized salt, filtered water, and optional ingredients like rice bran or ash, vinegar, garlic cloves, bay leaves, and peppercorns to enhance flavor and promote probiotic growth.
What equipment is essential for fermenting eggs?
Key tools include a glass jar with an airtight lid, a non-reactive bowl, measuring spoons and cups, a clean cloth or cheesecloth, a weight to keep eggs submerged, and sterilized tongs or a fork to avoid contamination.
How do I prepare eggs for fermentation?
Select fresh, uncracked eggs, gently rinse and inspect them, then lightly sanitize with a vinegar-water solution. Proper prep ensures safety and quality fermentation.
How long should fermented eggs be left to ferment?
Fermentation should last between 14 to 21 days. During this time, maintain brine levels and remove any surface scum daily for the best results.
How should fermented eggs be stored after fermentation?
After fermentation, refrigerate the eggs to slow the process and preserve freshness. Consume them within 1 to 2 months for optimal flavor and probiotic benefits.
What are some serving suggestions for fermented eggs?
Enjoy them as a snack, add to salads, grain bowls, noodles, or soups, and use as a garnish or condiment. Serve cold or at room temperature to retain flavor and probiotics.
What tips help ensure successful fermentation?
Use fresh, high-quality eggs, maintain the right brine concentration, keep eggs fully submerged, control fermentation temperature, and maintain cleanliness to achieve safe and flavorful results.
How can I troubleshoot common fermentation issues?
Address floating eggs by weighing them down, remove surface mold promptly, discard brine with off smells, avoid using cracked eggs, and adjust fermentation time for texture and flavor consistency.